Middle Cerebral Artery MCA. Cortical The superior upper or suprasylvian MCA branch gives rise to several arteries that supply much of the lateral and inferior frontal lobe and the anterior lateral parts of the parietal lobe.

Identify The Vessel Recognize The Stroke American Nurse
If a stroke occurs in this area you may see leg weakness andor difficulty thinking and making decisions.
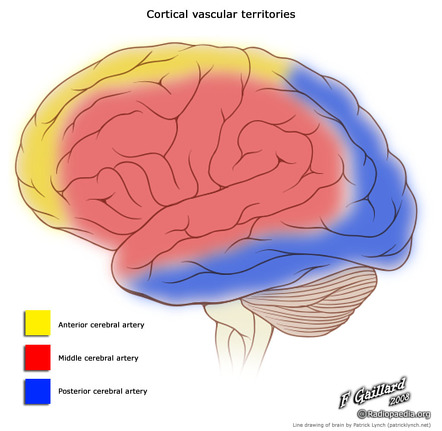
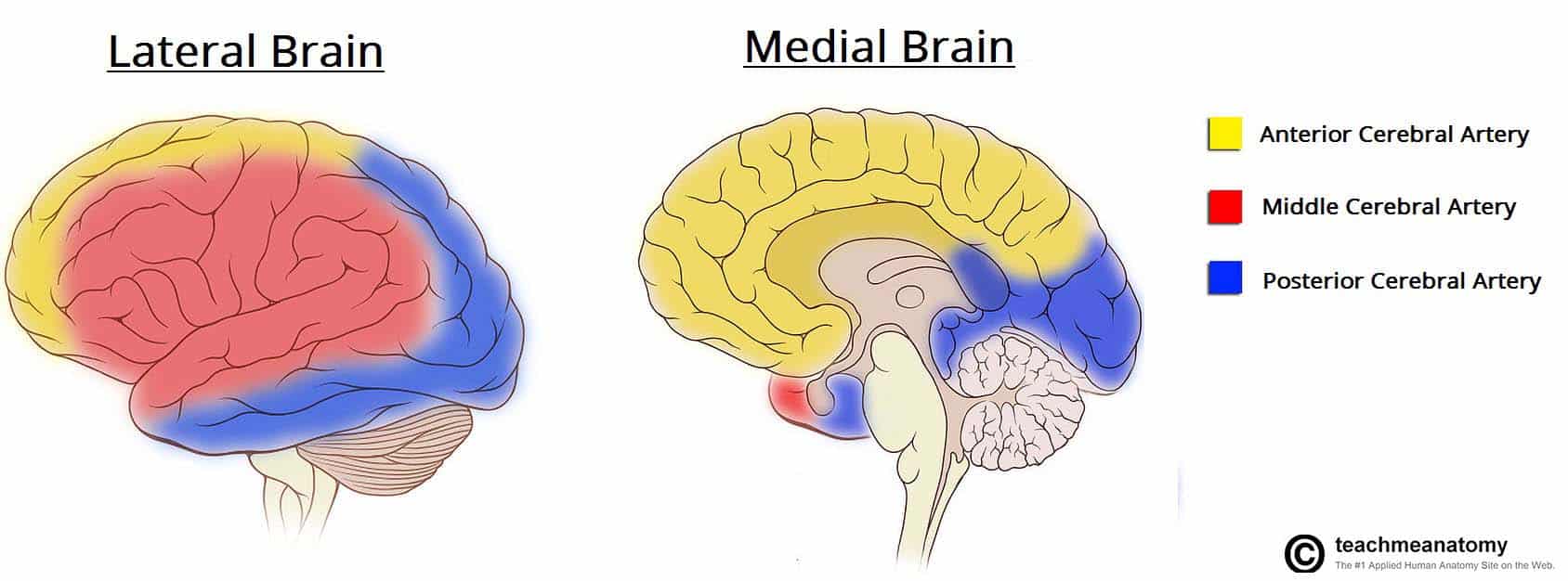
. The middle cerebral arteries are situated laterally supplying the majority of the lateral part of the brain. The primary venous drainage of the brain occurs via the internal jugular vein. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.
Anterior Cerebral Artery ACA. The middle cerebral artery MCA is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrumThe MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. Fig 14 Overview of the blood supply to.
The cortical branches of the MCA irrigate the brain parenchyma of the primary motor and somatosensory cortical areas of the face trunk and upper limbs apart from the insular and auditory cortex. The middle cerebral artery MCA is a terminal branch of the internal carotid artery and is part of the anterior cerebral circulation. There is a right sided AA and a left sided AA.
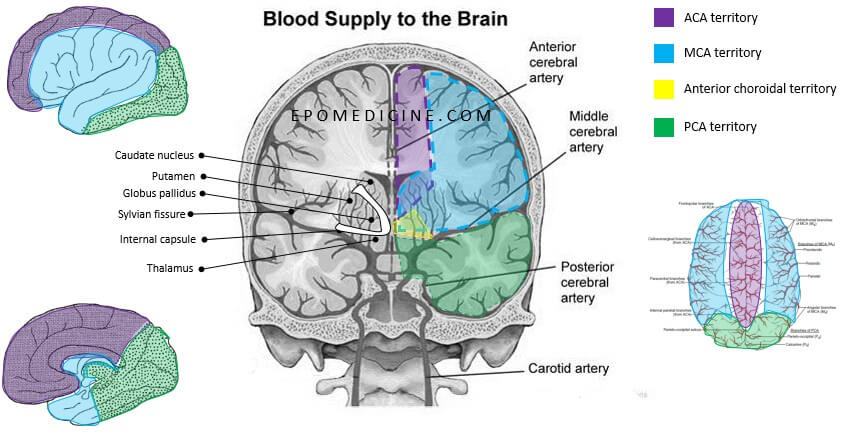
Diencephalon including thalamus subthalamic nucleus and hypothalamus Midbrain including cerebral peduncle third nerve and nucleus red nucleus and its connections superior cerebellar peduncle reticular formation. It travels from the base of the brain through the lateral sulcus of Sylvius before terminating on. There could also be changes in personality.
The left and right MCAs rise from. The posterior cerebral arteries supply both the medial and lateral parts of the posterior cerebrum. The carotid system supplies the brain from the internal carotid we demonstrate its terminal bifurcation into middle cerebral dark green and anterior cerebral bright green.
A narrow strip of the cerebral cortex about finger breadth adjoining superomedial border up to the parieto-occipital sulcus is supplied by anterior cerebral artery. The middle cerebral artery MCA is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the brain. This vessel supplies blood to the middle.
Penetrating branches of PCA participate in supplying the following key functional areas. The posterior circulation is derived from the vertebral arteries and consists primarily of the cerebellar and posterior cerebral arteries. The MCA supplies many deep brain structures the majority of the lateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres and the temporal pole of the brain.
The MCA also provides blood to the inner parts of the brain like the caudate internal capsule and thalamus. The middle cerebral artery is the largest branch of the internal carotid. The MCA supplies many deep brain structures the majority of the lateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres and the temporal pole of the brain.
Middle cerebral artery MCA is the larger terminal branch of the internal carotid artery ICA It supplies a large area of distribution as compare to the anterior cerebral artery ACA and posterior cerebral artery PCA2345 However the MCA supplies a wider area and has more cortical branches than the other two arteries literature does not provide detailed. Is derived from the internal carotid arteries and consists mainly of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. The middle cerebral artery MCA is the largest of the three major arteries that channels fresh blood to the brain.
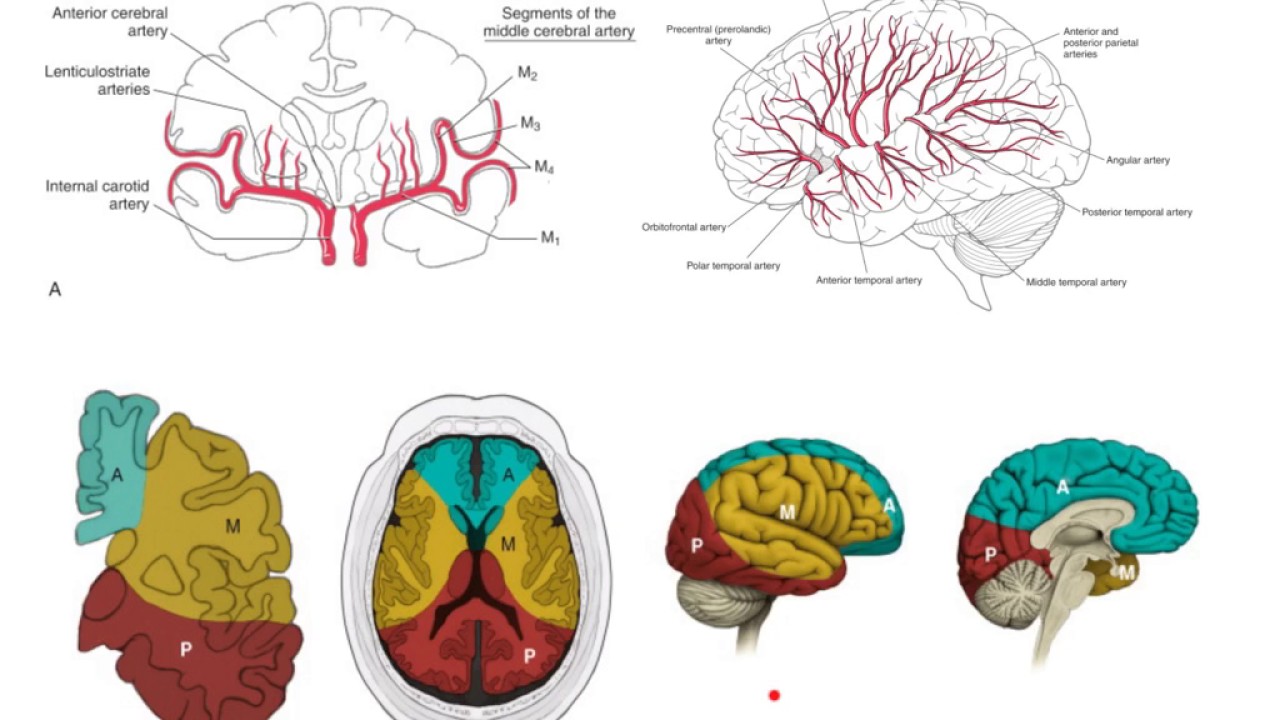
It subsequently divides to supply the lateral cortical surfaces along with the insula. Anatomically the MCA is. These arteries are vessels that provide blood supply to parts of the frontal temporal and parietal lobes of the brain.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is a terminal branch of the internal carotid artery and is part of the anterior cerebral circulation. The artery supplies a portion of the frontal lobe and the lateral surface of the temporal and parietal lobes including the primary motor and sensory areas of the face throat hand and arm and in the dominant hemisphere the areas for speech. The cortical branches of the MCA irrigate the brain parenchyma of the primary motor and somatosensory cortical areas of the face trunk and upper limbs apart from the insular and auditory cortex.
The middle cerebral artery arteria cerebri media is the largest of the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain 1. The anterior communicating artery runs between the two anterior cerebrals bright red The basilar artery pink is formed by the two vertebral arteries and it travels as. It travels through the Sylvian lateral fissure before coursing in a posterosuperior direction on the island of Reil insula.
The upper parts of primary motor and sensory areas are located in this region. The MCA supplies most of the outer convex brain surface nearly all the basal ganglia and the posterior and anterior internal capsules. The internal carotid artery consists of four main branches M1 M2 M3 and M4.
It branches off the internal carotid artery. They supply blood to the middle section of the frontal lobe the upper middle sections of the parietal lobe of the brain and to deep portions of the brain. The primary function of the MCA is to supply specific regions of parenchyma or functional brain tissue with oxygenated blood.
Anterior cerebral artery. The MCA branches throughout the brain. The posterior cerebral arteries supply both the medial and lateral parts of the posterior cerebrum.
This vessel supplies blood to the front part of your brain knows as your frontal lobe. This artery also supplies blood to the primary sensory and motor areas of the face hand throat and arm 2. The anterior cerebral artery is broken.
If a stroke occurs in this area you may see leg weakness andor difficulty thinking and making decisions. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery as the larger of the two main terminal branches the other being the anterior cerebral artery coursing laterally into the lateral sulcus where it branches to perfuse the cerebral cortex. The primary function of the MCA is to supply specific regions of brain parenchyma with oxygenated blood.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is the largest terminal branch of the internal carotid artery.
Middle Cerebral Artery Physiopedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13734/middle-cerebral-artery_english.jpg)
Middle Cerebral Artery Anatomy Branches Supply Kenhub

Middle Cerebral Artery Wikipedia

Middle Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Middle Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Circle Of Willis And Forebrain Blood Supply Epomedicine
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
0 comments
Post a Comment