Section views types of section views 1. Full section in a full section the cutting plane line passes fully through the part.
Engineering drawing views engineering drawing types INTRODUCTION.

. The second shows up well on complicated drawings. Break line is a thin continuous line and is drawn freehand. Section lines are used to define areas that represent where solid material has been cut in a sectional view.
The lines are thin and are usually drawn. These lines are called section lining or cross-hatching. Sectional views are used in technical drawing to expose internal surfaces.
An Elevation drawing is drawn on a vertical plane showing a vertical depiction. The Cutting-Plane Line The cutting-plane line represents the edge view of the cutting plane see Figure 8-3. The first form is more commonly used.
As the name suggests the section drawings show the structure in a sliced form. There are three major types of sections used in engineering drawing. In both cases the object should be standing on its base when the.
At each end of the line draw a short line with an arrow to show the direction for looking at the section. No need for additional orthographic views. Full section The view obtained even the cutting plane is right across the object.
6 Types of sectional views Full sections. Types of Sectional Views Full Section. Basic Components of an Engineering Drawing.
A plan drawing is a drawing on a horizontal plane showing a view from above. Concept example A section view is made by revolving the cross-section view 90 o about a cutting plane line and drawn on the orthographic view. 81 and it is required to draw three sectional viewsAssume that you had a bracket and cut it with a hacksaw along the line marked B-B.
Superimposed to orthographic view. Engineering drawings are often referred to as Blueprints. The line that separates the different types interior and exterior may be a.
A half-section is a view of an object showing one-half of the view in section as in figure 19 and 20. All the vertical lines stay vertical compared to front view and otherwise. A revolving view is effective for elongated objects or.
There is no cutting plane line. Figure 20 - Front view and half section. The cutting-plane line cuts halfway through the part and removes one quarter of the material.
Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD 2011 1e James Bethune. However the terms are becoming an anachronism since most copies of engineering drawings that were made using a chemical-printing process that yielded graphics on blue-coloured paper. Broken crosshatching shows where cutting plane line intersections material each material has its own crosshatching cutting plane line shows where the imaginery knife cuts thru the part line is always parallel to a line of rotation shows which.
There are three major types of sections used in engineering drawing. Sectional views in engineering technical drawings Half Sectional views. A cutting plane line shows where object was cut to obtain the section view.
Placement of a cross-section view 31. A full section is the most widely-used sectional view. Half Section is used to the exterior and interior of the part in the same view.
Types of Views in Engineering Drawing. A few of the more common ones are. What is Half Section.
Break from orthographic view. A short series of lectures on Engineering Drawing as Part of ENGG1960 By Paul Briozzo. In this type of section only half of the space or object is cut away.
Further section drawings also provide information for the types of materials to be used in the construction. Plan Section and Elevation are different types of drawings used by architects to graphically represent a building design and construction. Here is an object sectioned from two different directions.
Isometric drawings show parts as three-dimensional. Normally a view is replaced with the full section view. An elevation drawing is a view taken from a point outside the object without any slicing.
Gaskets seals Do not show hidden detail in sectional view. Figure 19 - Full and sectioned isometric views. A cutting plane does not necessarily need to cut the whole object.
Full sections half sections broken sections rotated. Section lines are evenly. ASME specifies two forms for cutting-plane lines as shown in Figure 8-4.
What is Full Section. A section drawing is a view taken after you slice an object then look at the surface created by the slicing. In this view the cutting plane is assumed to bend at a right angle and cuts through only half of the.
REVOLVED SECTION VIEW Revolved sections show cross-sectional features of a part. Example a a b b 30. BROKEN-OUT SECTION VIEW A break line is used to separate the sectioned portion from the unsectioned portion of the view.
The specific information a section shows may vary depending on whether it is a design or construction drawing. Partial or Broken Out Section 4. The diagonal lines on the section drawing are used to indicate the area that has been theoretically cut.
Half sections or views. Half sections are commonly used to show both the internal and outside view of symmetrical objects. There are a number of different types of sectional views that can be drawn.
K half section The view Obtained When the cutting plane goes half way across the Object to the centre line. A section is used to show the detail of a component or an assembly on a particular plane which is known as the cutting plane. - इजनयरग डरइग म सकशन क परकर 1.
Revolved section. You have learned that when making a multiview sketch hidden edges and surfaces are usually shown with hidden dash lines. When specific features of an object that need highlighting are not located.
This is the most common section called a full section with the imaginary laser cutting a line across. They serve to present additional orthographic views of surfaces. This kind of construction drawing helps identify the primary structures in relation to other surrounding structures of the building.
Types of Section in Engineering Drawing. A simple bracket is shown in Fig. Features that cannot be seen by hidden detail Cutting plane removes part section is what is left Cross hatching ois at 45 equispaced Centrelines often used for cutting planes Very thin sections not hatched eg.
The scale of section drawings may range from y to 3 317 mm to 76 mm depending upon the size of the drawing paper the size of the building or component and the desired features to be shown.
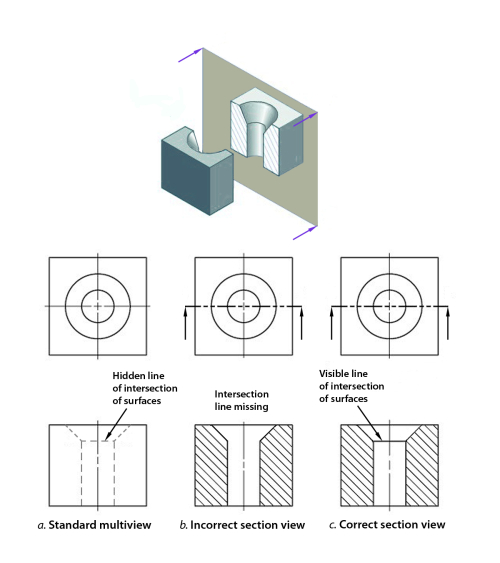
Sectioning Technique Engineering Design Mcgill University
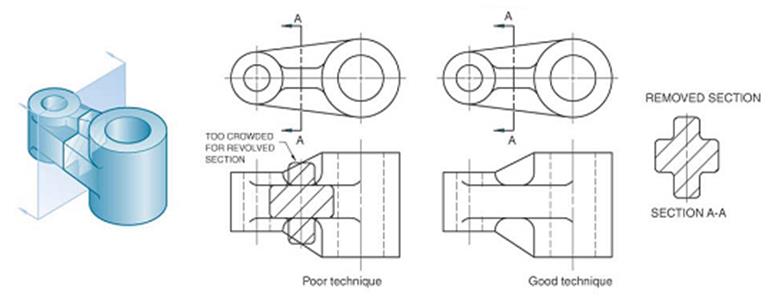
Sectional Views In Engineering Technical Drawings

Design Handbook Engineering Drawing And Sketching Related Resources Design And Manufacturing I Mechanical Engineering Mit Opencourseware
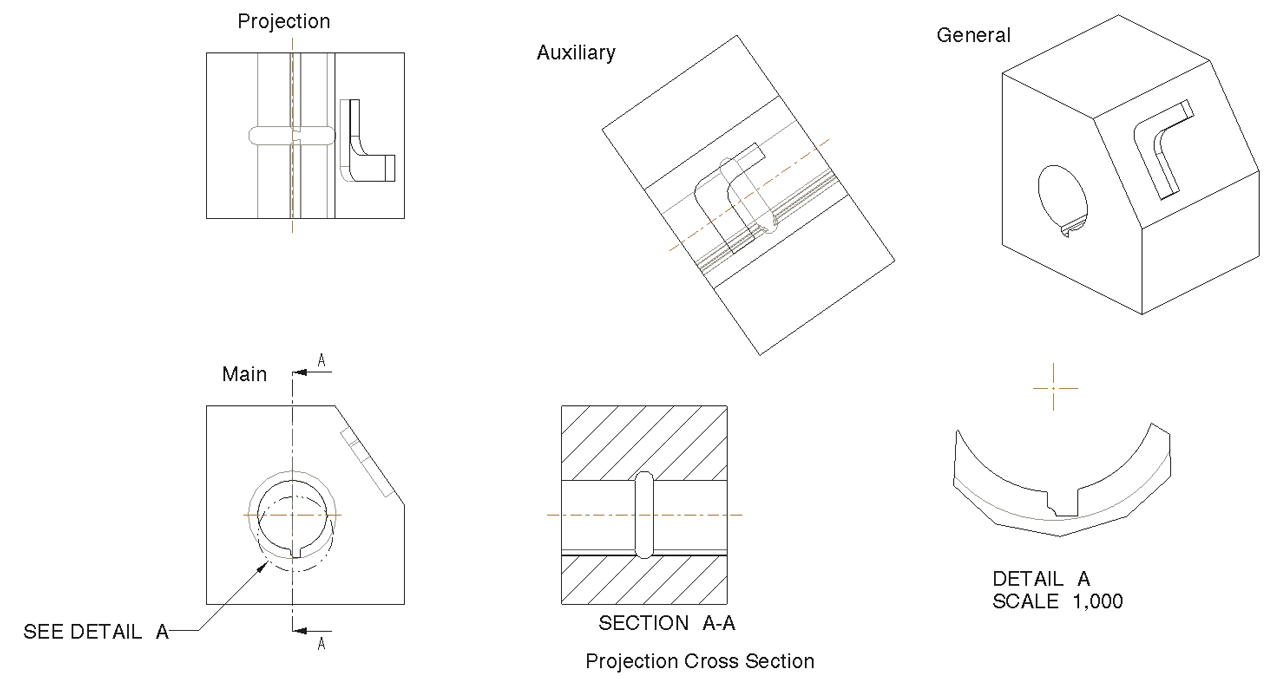
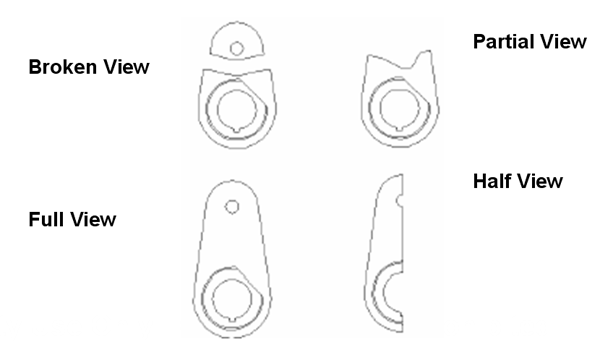
0 comments
Post a Comment